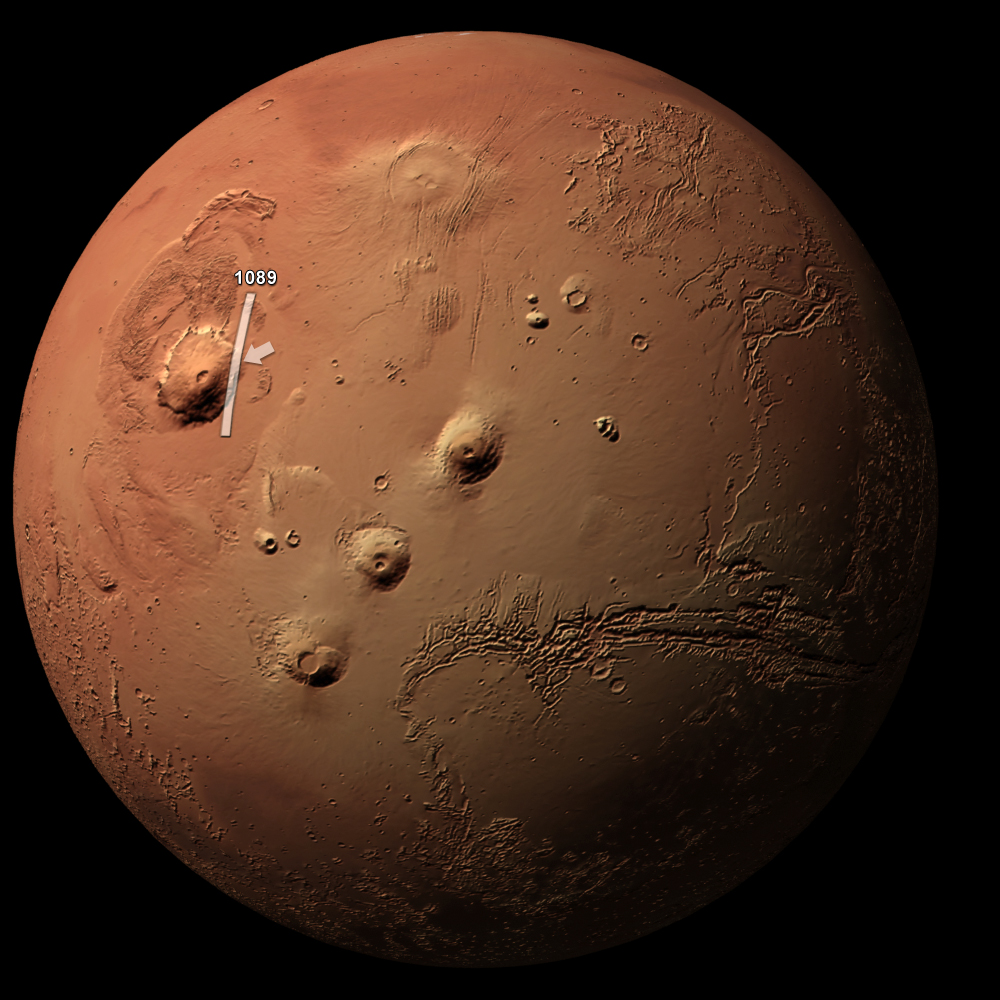
Mount Olympus Mons is a colossal shield volcano located on the planet Mars, towering over any volcano found on Earth. This extraordinary geological formation captures the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts alike, with its towering heights and expansive footprint. As the tallest planetary mountain in the solar system, Mount Olympus Mons stands at a staggering height of approximately 13.6 miles (22 kilometers), making it nearly three times the height of Mount Everest. Its size and structure provide valuable insights into the geological history of Mars and the processes that shaped its surface.
The awe-inspiring dimensions of Mount Olympus Mons are not just about its height; the volcano also boasts a diameter of about 370 miles (600 kilometers), making it roughly the size of the state of Arizona. A shield volcano forms from the repeated lava flows of low-viscosity magma, which allows the lava to travel great distances before solidifying. This unique formation process contributes to the gentle slopes of Olympus Mons, which contrast sharply with the steep cliffs that define its caldera. When combined with the planet's thin atmosphere, Mount Olympus Mons presents a fascinating subject for research in planetary geology.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of Mount Olympus Mons, we uncover not only its physical attributes but also the potential implications for future exploration and even colonization of Mars. Understanding this giant volcano opens a window into the planet's past and helps scientists piece together its climatic changes over billions of years. The exploration of Mount Olympus Mons could hold the key to answering questions about the possibility of life on Mars and the planet's geological activity.
What makes Mount Olympus Mons unique?
Mount Olympus Mons is not just another volcano; it is a marvel of planetary science. Here are some unique features that set it apart:
- **Height:** The sheer elevation of Olympus Mons is unmatched within our solar system.
- **Diameter:** With a diameter of approximately 370 miles, it is larger than any volcano on Earth.
- **Caldera:** The summit features a complex caldera, which is about 50 miles wide and contains multiple overlapping craters.
- **Flank Features:** The slopes of Olympus Mons are characterized by large lava flows and channels, indicating extensive volcanic activity.
How was Mount Olympus Mons formed?
The formation of Mount Olympus Mons is attributed to a series of volcanic eruptions that occurred over millions of years. The process can be summarized as follows:
- **Initial Eruptions:** Magma from the Martian mantle began to rise, leading to the initial construction of the volcano.
- **Repeated Lava Flows:** Low-viscosity lava flows spread across the surface, creating the broad, gentle slopes characteristic of shield volcanoes.
- **Caldera Formation:** As eruptions continued, the summit began to collapse, forming the large caldera we see today.
- **Continued Volcanism:** Evidence suggests that Olympus Mons may still be an active volcano with the potential for future eruptions.
What does Mount Olympus Mons tell us about Mars?
Mount Olympus Mons serves as a geological time capsule, providing insights into the history and evolution of the Martian surface. The study of this volcano allows scientists to:
- **Understand Volcanic Activity:** Investigate the volcanic processes that shaped Mars.
- **Climate Change:** Examine how volcanic eruptions may have influenced Mars' atmosphere and climate over time.
- **Potential for Life:** Explore the implications for past life on Mars, particularly in regions near volcanic activity.
Is Mount Olympus Mons a potential site for exploration?
As interest in Mars exploration grows, Mount Olympus Mons stands out as a prime candidate for future missions. The reasons for this include:
- **Scientific Research:** The volcano offers a unique opportunity to study Martian geology and volcanic processes up close.
- **Resource Utilization:** Exploring Olympus Mons may reveal valuable resources for future manned missions to Mars.
- **Potential for Colonization:** The diverse landscape and features may provide insights into establishing a human presence on Mars.
What challenges do scientists face in studying Mount Olympus Mons?
Despite the exciting prospects, studying Mount Olympus Mons comes with its own set of challenges:
- **Distance:** The vast distance from Earth makes it difficult to conduct real-time studies.
- **Technical Limitations:** Current technology may not be sufficient for detailed exploration of such a large structure.
- **Harsh Environment:** The Martian climate poses numerous challenges for landers and rovers designed to study the area.
What future missions might target Mount Olympus Mons?
Several upcoming missions to Mars may include Mount Olympus Mons as a focal point:
- **Mars Sample Return Mission:** A potential mission aiming to bring back samples from various locations, including Olympus Mons.
- **Mars Perseverance Rover:** Continuing exploration of the Martian surface with the possibility of targeting Olympus Mons in the future.
- **Crewed Missions:** NASA and private companies are planning future crewed missions to Mars, which may include Olympus Mons as a destination.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Mount Olympus Mons
Mount Olympus Mons is not just a geographical wonder but a significant key to understanding the history of Mars. Its unique features, formation history, and potential for future exploration make it a captivating subject for scientists and space enthusiasts alike. As technology advances and our ambitions to explore Mars grow, the mysteries of Mount Olympus Mons will undoubtedly continue to inspire generations to come.
Exploring The Hilarity Of The Discord Mod Meme
When Monkeys Get Thirsty: The Curious Case Of Monkey Drinking Powerade
Chloe Victoria Now: A Journey Through Time